Move JX Command
Overview
The JX command helps the robot to move to the target position (pos) within the joint space. Since the target position is inputted as a posx form in the task space, it moves in the same way as movel. However, since this robot motion is performed in the joint space, it does not guarantee a linear path to the target position.
In addition, one of 8 types of joint combinations (robot configurations) corresponding to the task space coordinate system (posx) must be specified in sol (solution space).
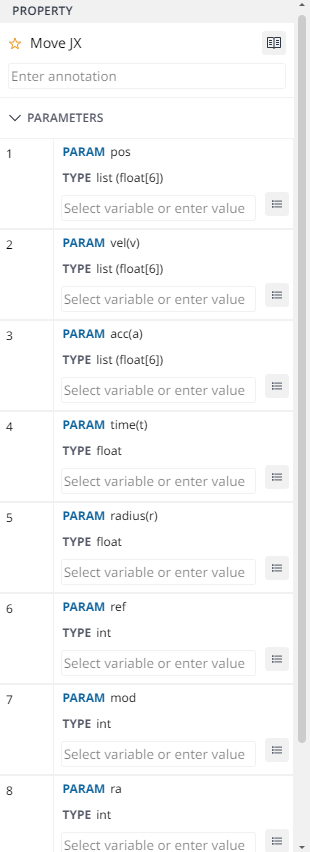
Property
Annotation
You can insert text in the description, unique meaning, or nickname for each Parameter to differentiate with many DRL Components.
Parameters
In Parameter Panel, it will help you create or select your variable to define the parameter of the chosen command.
For detailed DRL description other than parameter, please refer to the following online manual link: https://manual.doosanrobotics.com/help/programming/2.9/publish/en_us/movejx-13682520.html.
Parameter Name | Data Type | Default Value | Description |
pos | posx | - | posx or position list |
list (float[6]) | |||
vel (v) | float | None None | velocity (same to all axes) or velocity (to an axis) |
list (float[6]) | |||
acc (a) | float | None None | acceleration (same to all axes) or acceleration (acceleration to an axis) |
list (float[6]) | |||
time (t) | float | None | Reach time [sec] |
radius (r) | float | None | Radius for blending |
ref | int | None | reference coordinate ž DR_BASE: base coordinate ž DR_WORLD: world coordinate ž DR_TOOL: tool coordinate ž user coordinate: User defined |
mod | int | DR_MV_MOD_ABS | Movement basis ž DR_MV_MOD_ABS: Absolute ž DR_MV_MOD_REL: Relative |
ra | int | DR_MV_RA_DUPLICATE | Reactive motion mode ž DR_MV_RA_DUPLICATE: duplicate ž DR_MV_RA_OVERRIDE: override |
sol | int | 0 | Solution space |
Example
DRL Code
P0 = posj(0,0,90,0,90,0)
movej(P0, v=30, a=30)
P1 = posx(400,500,800,0,180,0)
P2 = posx(400,500,500,0,180,0)
movel(P2, vel=100, acc=200) # Linear movement to P2
X_tmp, sol_init = get_current_posx() # Obtains the current solution space from the P2 position
movejx(P1, vel=30, acc=60, sol=sol_init)
# Moves to the joint angle with a velocity and acceleration of 30(deg/sec) and 60(deg/sec2), respectively,
# when the TCP edge is the P1 position (maintaining the solution space in the last P2 position)
movejx(P2, time=5, sol=2)
# Moves to the joint angle with a reach time of 5 sec when the TCP edge is at the P2 position
# (forcefully sets a solution space to 2)
movejx(P1, vel=[10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60], acc=[20, 20, 30, 30, 40, 40], radius=100, sol=2)
# Moves the robot to the joint angle when the TCP edge is at the P1 position,
# and the next motion is executed when the distance from the P2 position is 100mm.
movejx(P2, v=30, a=60, ra= DR_MV_RA_OVERRIDE, sol=2)
# Immediately terminates the last motion and blends it to move to the joint angle
# when the TCP edge is at the P2 position.